Every chain handles hundreds of cryptocurrency transactions every day. But where does all this crypto come from? It doesn’t just appear out of thin air, but follows its own logic. Knowing how supply grows, and why certain assets gain value over time can help lift some of the mystery around tokens. They can be created through staking, minted from digital files (like NFTs) or generated by smart contracts. Today we’re going to talk about minting and how it works.
Table of Contents
What Minting Means in Crypto
Minting is the process of creating new digital assets on a blockchain. New cryptocurrency coins and brand-new NFTs are all minted. It’s how tokens come into existence and become part of the network.
How Minting Works for Coins and Tokens
Minting works differently for various types of digital assets.
- Cryptocurrency Minting: This is when new coins are created and added to a blockchain. It usually happens through mechanisms like proof-of-stake, where validators help secure the network and earn newly minted coins as a reward. It’s basically how a blockchain grows its supply.
- NFT Minting: Minting a non-fungible token (NFT) means turning a digital file—like art, music, or an in-game item—into a unique asset on the blockchain. Once minted, it gets its own ID, making it verifiable, tradable, and provably yours.
- Smart Contract Minting: Some tokens are minted automatically through smart contracts. These contracts follow preset rules and create new tokens whenever certain actions happen—like joining a game, staking assets, or buying an item—removing the need for any middleman.
Minting vs. Mining vs. Staking
Crypto minting is easy to mix up with crypto mining or staking. Each process is connected to crypto and coins, but their purpose is different. Here’s a table that makes it easy to tell these three terms apart.
| Category | Minting | Mining | Staking |
| Purpose | Create new tokens/NFTs | Add new blocks + create coins | Secure network + earn rewards |
| How It Works | Smart contracts or PoS rules create assets | Solve puzzles with hardware | Lock tokens to validate transactions |
| Energy Use | Low | Very high | Low |
| Requirements | Wallet + platform | GPUs/ASICs + high power use | Tokens to stake |
| Rewards | Newly minted tokens/NFTs | Block rewards | Staking yield |
| Risks | Smart contract issues | Hardware cost + volatility | Slashing or losing staked assets |
Key Features of Minting
- Token Creation: When people ask “what is minting in crypto?”, this is the part they usually mean. Minting is the process of creating new tokens or cryptocurrency coins on a blockchain network. No actual physical coins are created! Instead, the blockchain adds a new block and records the creation of a newly minted cryptocurrency on its digital public ledger. This process can work through different consensus mechanisms, such as proof-of-stake (PoS), where users stake tokens instead of relying on the heavy computational power required in crypto mining.
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts can automate the minting process. They follow preset rules that determine when new tokens are created, how many can exist, and who receives them. These contracts also help validate transactions and verify data, making sure everything is recorded correctly on the decentralized ledger. Whether you’re minting coins, distributing rewards, or creating a new token for a project, the smart contract ensures the system runs without a middleman and with full transparency.
- NFT Creation: Minting also applies to non-fungible tokens (NFTs). Here, the process involves taking a digital file—like artwork, music, or an in-game item—and turning it into a unique token on the blockchain. Once minted, the NFT becomes a digital asset with verifiable ownership that can be traded on an NFT marketplace. Each new NFT is recorded as a permanent entry on the blockchain, proving its authenticity and giving creators a simple, secure way to bring digital artwork into the crypto ecosystem.
Costs, Chain Choices, and Examples
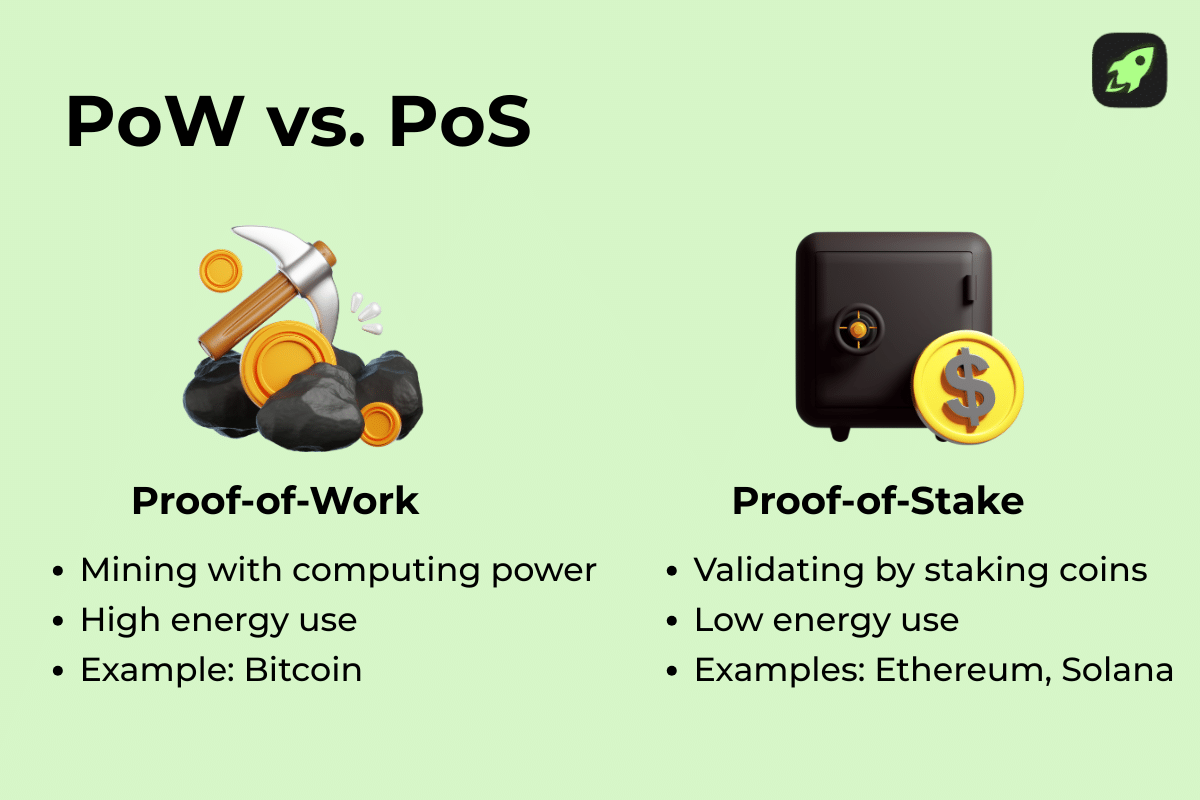
When you mint cryptocurrency or NFTs, the cost depends on the blockchain network you choose and how that network validates transactions. On blockchains that use proof-of-work (PoW), the minting process can be expensive because it requires specialized hardware, a lot of computational power, and high transaction fees. In contrast, proof-of-stake (PoS) chains like the Ethereum network (after its upgrade) or other PoS chains such as Solana and Polygon, offer a more environmentally friendly and affordable way to mint cryptocurrency, since system users simply stake tokens instead of running energy-heavy machines. Each chain also has its own native token used to pay fees when adding transactions or creating a new block.
For example, minting an NFT on the Ethereum blockchain can cost more during busy hours, while minting on Polygon or Solana is much cheaper and faster. On top of that, the upfront cost for crypto minting on PoS chains—where new coins are minted as staking rewards—is minimal compared to PoW mining, which usually requires a larger investment. Choosing the right chain affects the price, speed, security, and the overall experience.

How to Get Free Crypto
Simple tricks to build a profitable portfolio at zero cost

Benefits of Minting
Minting crypto comes with several advantages, especially as more users show interest in decentralized finance (DeFi). One major benefit is accessibility: while crypto mining requires expensive hardware and a significant amount of computational work, many proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchains let you mint cryptocurrency with minimal investment by simply staking tokens. The minting process also supports the creation of new coins and new blocks, helping the network stay secure as smart contracts validate transactions automatically.
Another benefit is efficiency—minting on PoS is a far more sustainable alternative to energy-heavy mining. Plus, for creators, minting NFTs allows anyone to turn digital work into verifiable blockchain assets.
Overall, minting crypto gives users more control, lower costs, and a simple way to participate in the growth of new cryptocurrencies.
Risks and Limitations
While minting crypto has plenty of benefits, it also comes with risks that beginners should understand. Even on proof-of-stake networks, the minting process still requires you to lock up funds—and you risk losing your staked tokens if the network penalizes mistakes or dishonest behavior.
On the proof-of-work side, minting (or mining) demands hardware, high energy use, and upfront costs. Smart contract–based minting carries its own dangers: buggy code, high transaction fees, or malicious contracts can lead to lost assets. And even though minting helps create new coins and supports decentralized finance, the process still requires some technical knowledge to avoid errors.
If you mint cryptocurrency or NFTs without understanding the chain, gas fees, or consensus mechanism, you could easily overpay, mint on the wrong network, or lose access to your new cryptocurrency entirely.
Use Cases
Because minting is such an integral part of the crypto ecosystem, its use cases now go far beyond coins. Here’s how different industries use the minting process today:
Digital Art and Collectibles
In the NFT world, the term minting describes turning a digital file into a blockchain asset. A smart contract locks in ownership, and the blockchain verifies transactions every time the item is sold or traded. This removes fake copies and gives creators permanent credit for their work. The main difference from traditional digital art is that collectors actually own the item on-chain. Because blockchain adds new blocks to record each transfer, the artwork becomes part of a secure, publicly visible history, trusted by many users.
Virtual Real Estate and Gaming Items
Games and metaverse platforms mint land plots, characters, and in-game items so players can truly own them. Instead of relying on a company server, the blockchain handles validating transactions and recording them in randomly chosen blocks, depending on the consensus mechanism—often proof-of-stake rather than energy-heavy crypto mining. Players can buy, sell, and trade assets freely, and the blockchain ensures each item remains unique. This system gives gamers more freedom, value, and portability across platforms.
Music, Licensing, and Identity Assets
Minting helps musicians and creators tokenize songs, licenses, and certificates. Once minted, these assets become tamper-proof entries that the network can validate quickly. This reduces fraud, enables direct ownership for fans, and creates new royalty models. Identity credentials can also be minted to make verification safer and faster.
Stablecoins and Token Minting
Often, stablecoins are created through crypto minting, where a certain amount of tokens is minted when collateral is deposited into a protocol. Instead of generating cryptocurrency through mining, stablecoin systems mint tokens at high speed using on-chain rules. Each new coin appears only after the protocol adds a block confirming the deposit.
Final Thoughts
Minting might seem technical at first, but once you break it down, it’s simply the way new blockchain assets come to life. If you’re minting coins, NFTs, or tokens, the process always comes back to the same core idea: adding data to a blockchain in a secure, verifiable way. Every time the network verifies transactions, creates new blocks, or rewards individual staking, minting plays a role. It’s the quieter counterpart to crypto mining, but it’s just as important for keeping transactions flowing and the system moving.
Through different mechanisms—from PoS staking to automated smart contracts—minting allows the crypto ecosystem to grow without relying on the heavy computational work of mining. Instead of waiting for the first miner to solve a puzzle, minting often uses simpler, more efficient processes that still provide proof the network can trust. Each block added, each asset created, and each new token minted becomes part of the shared, public page that makes blockchain transparent.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.


