Staking locks up your coins, and that can feel frustrating. Your staked assets are earning rewards on the Ethereum network, but they’re also just sitting there. That’s where restaking comes in. With a restaking protocol, your staked assets can secure multiple protocols and services at once, picking up additional rewards, while your assets remain secure.
If you’re looking to get as many potential rewards from your assets as possible, you’ve come to the right place. In this article, we’ll figure out how restaking works, why it matters, and what you need to watch out for.
Table of Contents
What Is Restaking?
Restaking means taking coins you’ve already staked on a proof-of-stake (PoS) blockchain and re-committing to other services through a restaking protocol. This links your tokens to new smart contracts that allow them to be re-used to support multiple protocols or decentralized applications at once. Your assets still back the original network, but they also take on extra roles.
It’s not the same thing as regular staking, in which your digital assets only validate one chain at a time. And it isn’t just liquid staking, where you get a token like stETH or rETH that represents your deposit. Restaking is broader than that: it reuses your staked assets to increase the security of more decentralized finance services alongside the base chain.
Restaking is already growing fast. EigenLayer, the most popular protocol for restaking, holds over $20B in TVL as of August 2025. That’s solid proof that this technology is going to keep growing in the future.
What Is the Difference Between Restaking and Staking?
Both traditional staking and restaking lock up your crypto, but they serve different purposes. Staking ties your assets to a single PoS blockchain. Restaking lets those assets work across several protocols at once, and earn additional rewards that way.
| Aspect | Staking | Restaking |
| Definition | Locking coins to support a single PoS blockchain network | Reusing staked coins through a restaking protocol to secure several decentralized services |
| Main Goal | Keep the base chain running and earn rewards | Increase capital efficiency by using the same stake for extra activity |
| Rewards | Standard staking rewards paid by the base chain | Additional rewards from other services on top of the original gains |
| Risks | Loss of funds only if slashing happens on the base chain | More slashing conditions, correlated slashing, smart contract and governance risks |
| Flexibility | Funds locked until the unbonding period ends | Same lock-up rules, plus any delays imposed by the protocol |
| Who’s Involved | Validators run nodes; delegators assign a stake | Validators or node operators run decentralized services; delegators assign a stake |
How Restaking Works
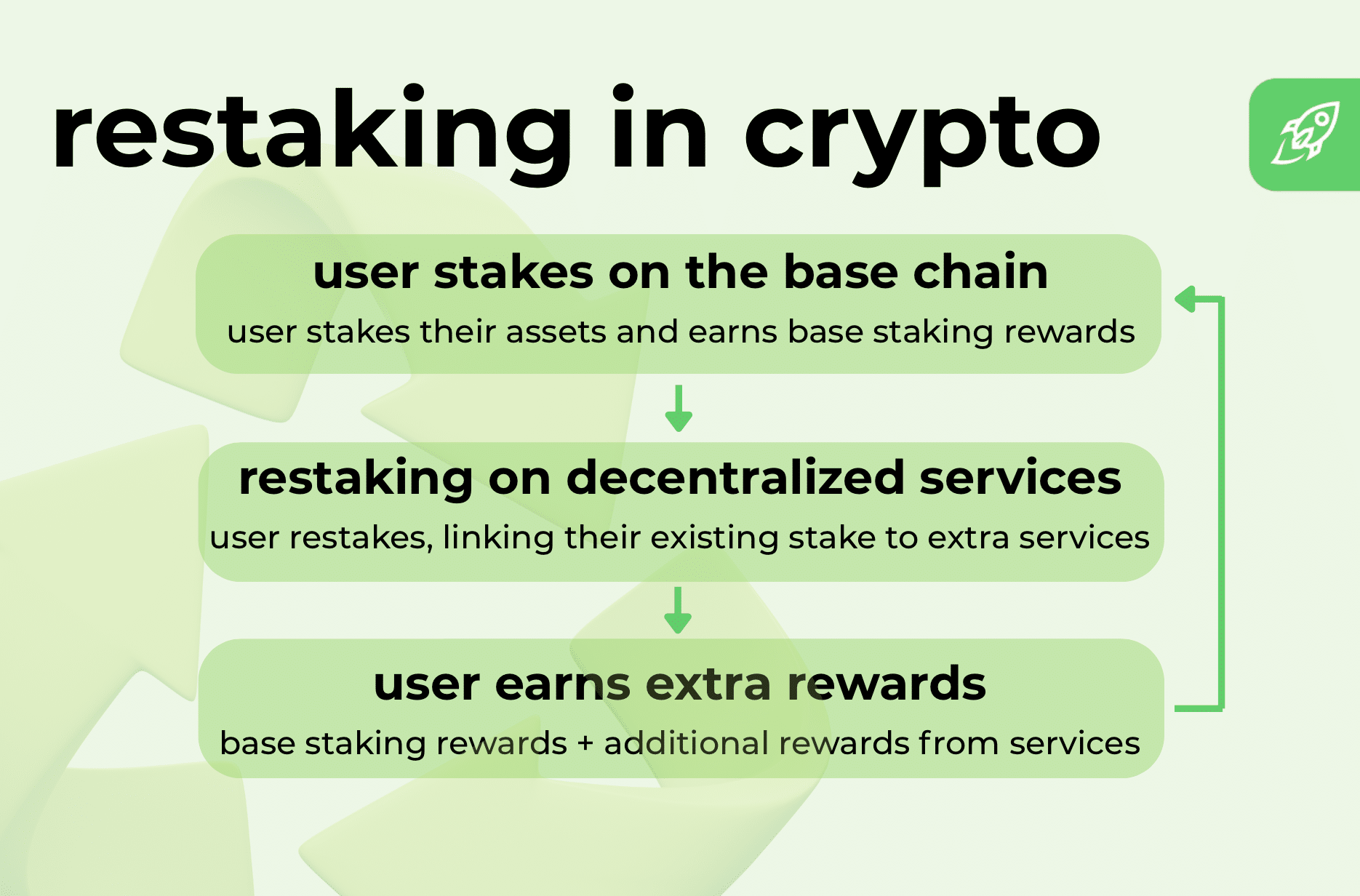
Restaking is built on smart contracts that allow staked assets to be used in more than one service or decentralized protocol. The contracts handle deposits, keep track of where funds go, and apply slashing rules if someone misbehaves.
You can restake in two main ways. If you run a validator on Ethereum, you can connect directly through a protocol like EigenLayer—that’s native restaking. But if you don’t run hardware, you can restake with liquid staking tokens (LSTs) such as stETH from Lido, or rETH from Rocket Pool. In this case, you act as a delegator, passing tokens to a node operator who does the heavy lifting.
Restaked assets are then pointed to various services: Oracle networks that feed in outside data, data availability services for rollups, rollup sequencers that order transactions, or verifiable computation services that run complex calculations off-chain and prove the results on-chain. In this system, operators choose what to run, and delegators decide who to trust. Everyone gets the base rewards, plus additional yield for securing various services with their restaked assets.
The EigenLayer ecosystem is the most popular example of restaking in action. It accepts ETH and major liquid staking tokens, then routes them into “Actively Validated Services” (AVSs) like EigenDA for rollup data. As we’ve seen, the TVL of EigenLayer as of August 2025 is over $20B. That popularity shows how quickly restaking has been adopted across the DeFi ecosystem as a way to boost capital efficiency.
Why Is Restaking Important?
Restaking matters because it makes your staked assets more useful. Instead of locking them into a single blockchain, you can extend their role to multiple protocols at once. That means more capital efficiency, enhanced security, and greater liquidity, all without having to move your coins.
Capital efficiency comes from reusing the same collateral across several projects. By pooling ETH from Ethereum’s base layer, this collateral efficiency saves new protocols from raising huge sums just to protect themselves.
Security means protocols can tap into Ethereum’s cryptoeconomic security budget, instead of building everything from scratch, which cuts costs and speeds up development. Projects don’t need to compete for validators, instead they collectively help secure the network, strengthening both Ethereum and the services it anchors.
Liquidity rises as restaked assets move through different platforms instead of sitting idle. Their flow helps stabilize token markets and keeps funds available for new uses across the DeFi ecosystem.
Overall, restaking matters because it expands the power of your digital assets, which drives efficiency, security, and liquidity across the whole ecosystem.
Learn how to spot scams and protect your crypto with our free checklist.

The Benefits of Restaking
With restaking, you can earn more from your staked assets while helping support network security across several places at once. Flexibility is another key benefit, enabling users to keep their tokens active on the base chain and other protocols, without needing to unstake or sell them to chase new opportunities. Then there’s the upside—let’s take a look in more detail.
Improved Rewards for Stakers
The clearest benefit of restaking is better yield. You can earn the base chain’s rewards, and also pick up extra from the services you back through restaking. In some setups, that means a higher risk premium, which is extra compensation for taking on more responsibility.
For example, ETH staked through Lido (stETH) or Rocket Pool (rETH) can be restaked into the EigenLayer ecosystem using those liquid staking tokens. Once there, it may support an oracle network or a data availability service, generating new payouts on top of Ethereum’s rewards. Protocols often issue liquid restaking tokens (LRTs) to track these deposits, which you can move into other parts of DeFi for even more yield.
This layering is sometimes called rehypothecation, and while it boosts potential returns, it also introduces extra risk, which is what we’ll discuss next.
The Risks of Restaking
Restaking isn’t just free money. By spreading your staked assets across so many protocols, you open the door to many new risks. Here’s what you need to watch out for:
Slashing
The biggest risk in restaking is slashing: losing part of your stake if any rules are broken. In normal staking, validators can be slashed for downtime or double-signing. In restaking, the danger grows because your funds are tied to even more slashing conditions. If a node operator misbehaves across multiple services, for example, it can trigger correlated slashing, cutting a large portion of funds at once. This is why delegators must choose operators carefully.
Yield Risks
Returns from restaking aren’t guaranteed. While you keep earning base staking rewards, the extra income depends on each Actively Validated Service involved. If a service underperforms, or if its smart contracts fail, your extra payout may shrink, or even disappear. In some cases, projects use rehypothecation (restaking the same tokens again), which amplifies both yield and risk. Market swings and low liquidity can also hurt the value of LRTs, changing their final values.
Impact on the Layer 1 Blockchain
Restaking also affects the Layer 1 blockchain itself. On Ethereum, critics including Vitalik Buterin have warned that loading too many duties on validators could stretch the consensus layer. In late 2023, Ethereum developers even introduced EIP-7514 to slow validator growth, partly out of concern for restaking’s impact on the base chain. If validators concentrate around big providers like Lido or Rocket Pool, the system risks increased centralization. This creates governance issues and reduces the resilience of the chain.
Tools & Platforms for Restaking
Restaking has grown thanks to a few major platforms. Each one gives you different ways to use your staked assets and earn rewards. Together, these projects form the core of today’s restaking ecosystem.
- EigenLayer: The core restaking protocol built on Ethereum. It lets you restake ETH or LSTs, and delegate to node operators who run AVSs such as oracles, data availability services, or rollup sequencers.
- Ether.fi: A leading liquid restaking platform. You deposit ETH or stETH and get back eETH, which you can use across the DeFi ecosystem while your stake is restaked through EigenLayer. It holds around $12B TVL as of August 2025.
- Renzo: Another liquid restaking project. It issues ezETH when you deposit ETH or LSTs. Its Total Value Restaked is just above $1.5B as of August 2025.
- Puffer Finance: Lets you restake ETH and mint pufETH. It offers added slashing protection and validator-friendly tools.
- Kelp DAO (Kernel DAO): Offers rsETH, one of the first multi-chain restaking tokens.
- Mellow LRT: Built on Symbiotic, an EigenLayer competitor. Focuses on structured vaults for different risk levels. It’s currently approaching $500M in TVL.
- Swell (rswETH) & Eigenpie: Both issue LRTs (such as rswETH for Swell) that you can use in decentralized finance while still earning rewards in EigenLayer.
Final Thoughts: Is Restaking Worth It?
Yes, but only if you understand the trade-offs. Restaking can turn your staked assets into a source of extra rewards across lots of protocols, boosting capital efficiency and adding flexibility. For many investors, that’s an attractive upgrade over traditional staking.
But higher yield comes with higher risks. You’re not just exposed to Ethereum’s rules anymore, you’re also tied to each individual protocol, its smart contracts, and the extra slashing conditions that come with them. If any validator or node operator fails, your coins could be on the line.
This is the bottom line: restaking offers real benefits, like stronger network security, more liquidity, and better utility for the same assets. At the same time, it adds complexity and new failure points. If you’re exploring it, start small, pick trusted platforms like EigenLayer, and never commit more than you’re ready to lose.
FAQ
Is restaking the same as staking twice?
No. Regular staking locks your coins to a single proof-of-stake blockchain. Restaking doesn’t mean “staking twice”—that isn’t possible. It reuses the same assets through a restaking protocol, extending them to support other protocols without creating a second stake.
Can I lose my crypto if I restake?
Yes. You still face normal slashing risks from the base chain, but restaking adds even more. Extra slashing conditions, smart contract risks, or operator mistakes can cut into your funds.
Is restaking only available for Ethereum?
Right now, most activity is on the Ethereum network through EigenLayer. Other PoS blockchains may add it in the future, but Ethereum is the main hub for today.
Can I undo a restake and get my crypto back?
Yes, but not instantly. Protocols enforce an unbonding period, and some add extra delays. This waiting time helps catch misbehavior before the restaking process is marked complete.
Why would anyone choose to restake if it’s riskier?
Investors restake because there’s a chance of earning extra rewards and improving their capital efficiency. With careful choices, they can lift their returns quite a lot. At the same time, operators and protocols respond to rising demand for flexible options by leaning on restaking as a practical tool.
Disclaimer: Please note that the contents of this article are not financial or investing advice. The information provided in this article is the author’s opinion only and should not be considered as offering trading or investing recommendations. We do not make any warranties about the completeness, reliability and accuracy of this information. The cryptocurrency market suffers from high volatility and occasional arbitrary movements. Any investor, trader, or regular crypto users should research multiple viewpoints and be familiar with all local regulations before committing to an investment.



Restaking makes you around 20% apy on cosmos that’s like a lot
you hear about this all the time on crypto twitter. i guess this is my sign to finally go and try it
yo i heard you like staking so i put restaking in your staking so you can restake while you stake
The only good reason to restake is when you need returns quicker than initial stake